Products
Our product portfolio
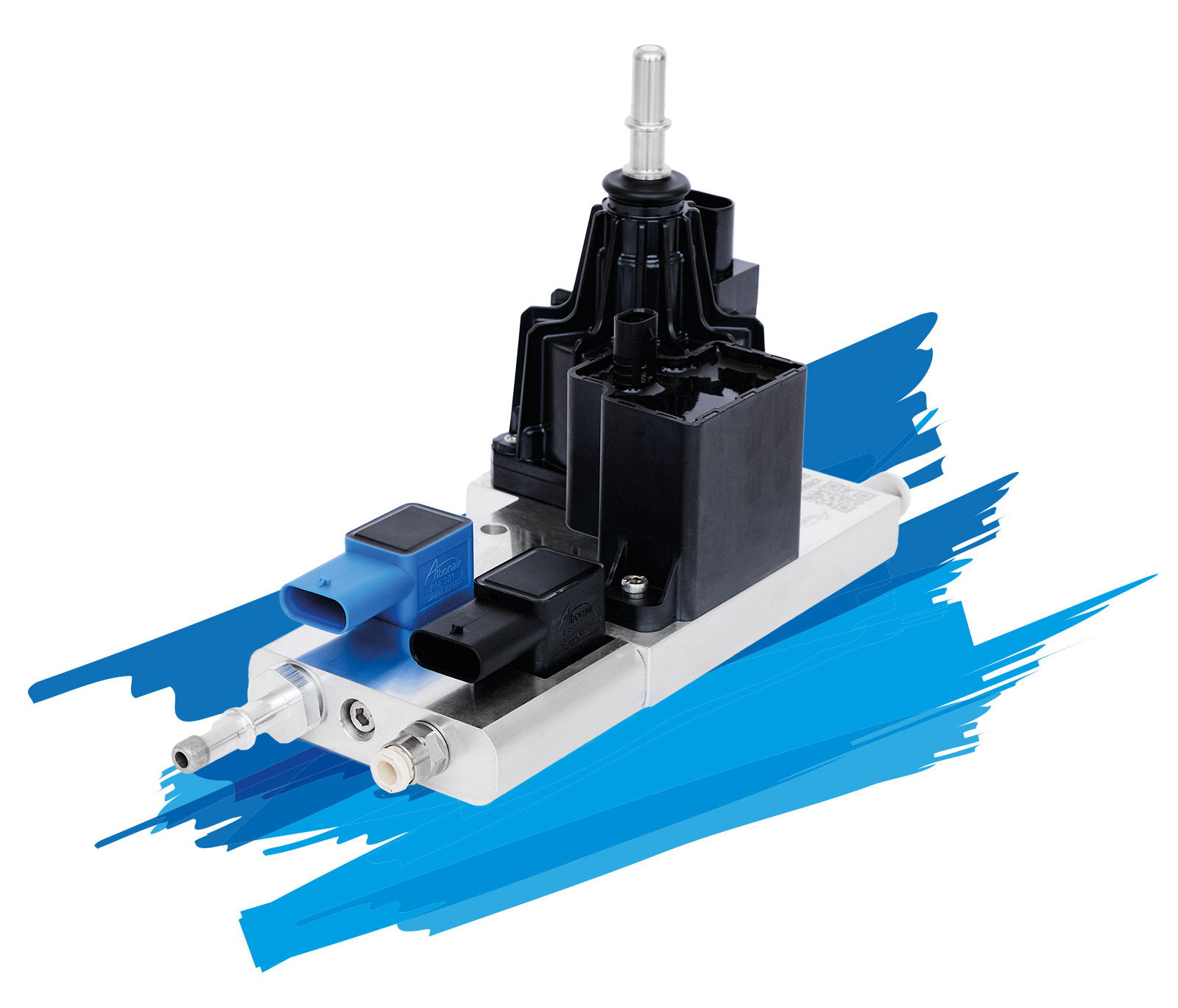
Dosing units
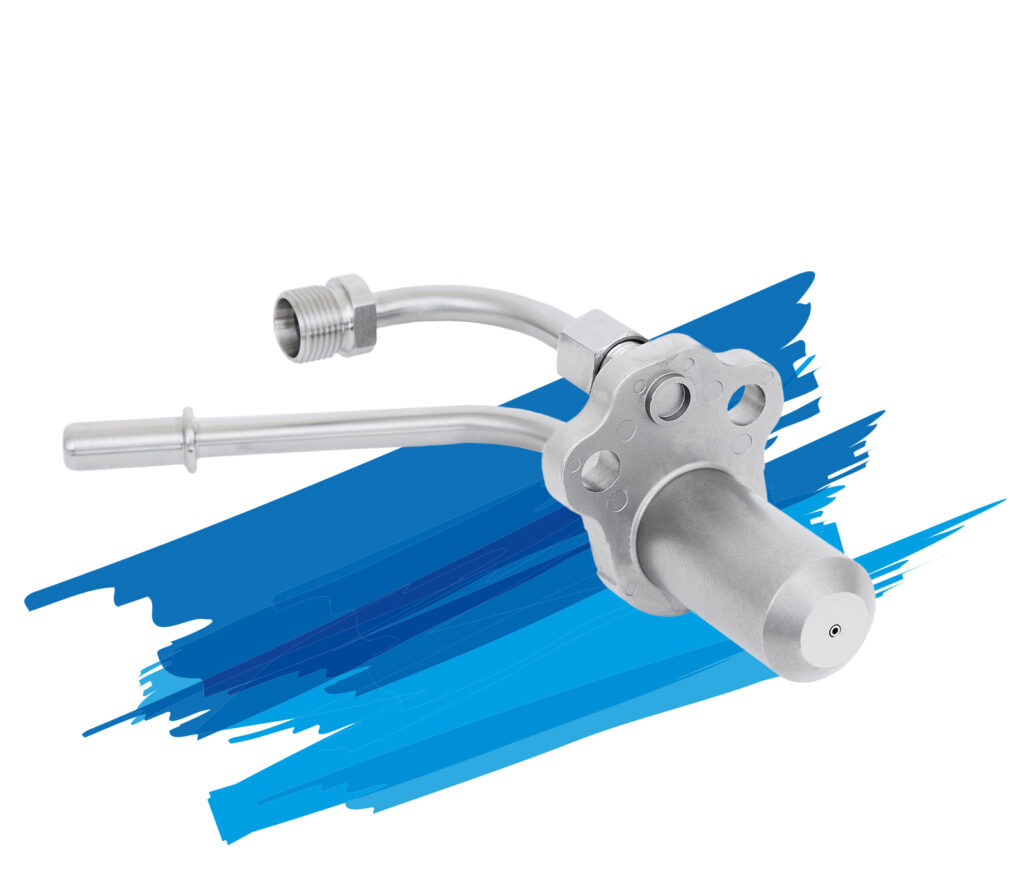
Nozzles

Thermal management systems
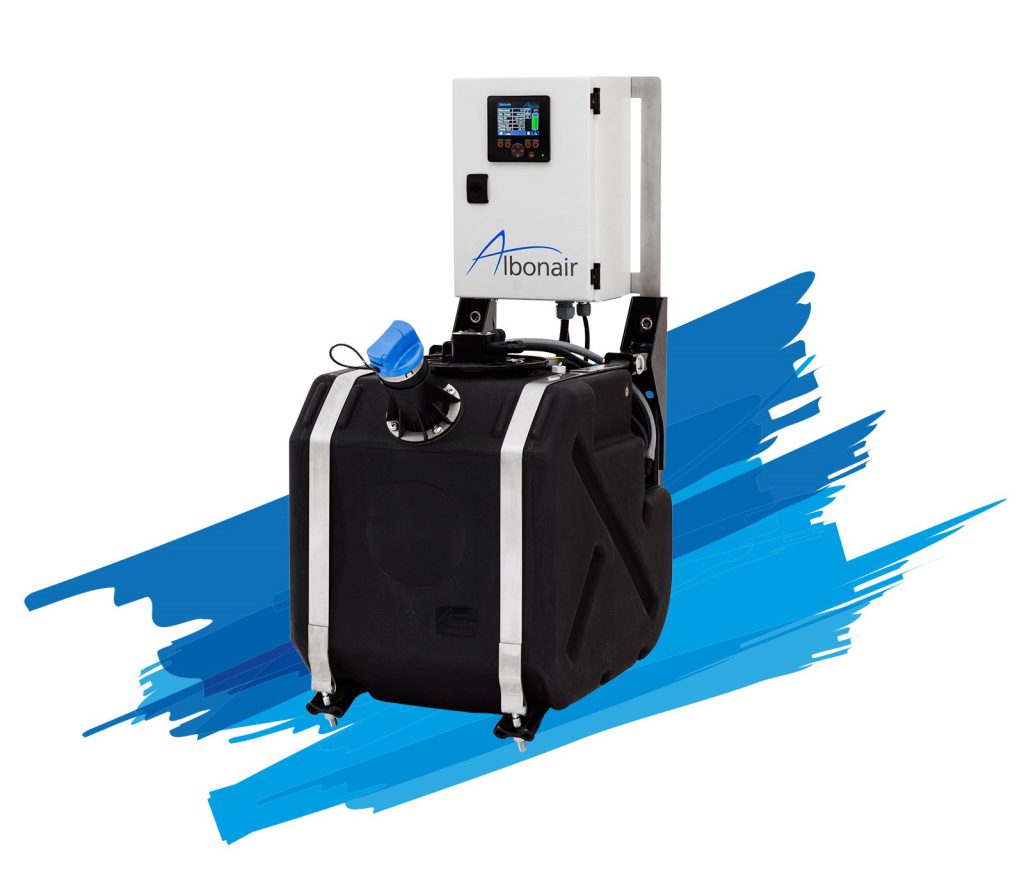
Systems for stationary systems

Specialist for exhaust aftertreatment
Albonair is a specialist in the development and manufacturing of urea dosing systems. Thermal management systems also complement our product portfolio.
As an automotive-certified series supplier, we support our customers as a competent provider when it comes to exhaust aftertreatment. Albonair’s focus is on the commercial vehicle sector. With our products, we offer vehicle and engine manufacturers innovative solutions for compliance with statutory emission standards in the on-road and off-road sector.
Well-known manufacturers such as Volvo, Renault and Liebherr rely on Albonair’s expertise. With a market share of over 25 percent for Euro VI vehicles, our company is one of the major players in the European market.

Albonair is also prepared for future standards and, as a reliable partner, develops tailor-made solutions for the specific system requirements of its customers. Our outstanding technologies make an important contribution to the environmentally friendly mobility of tomorrow, because the combustion engine will remain as one of the main types of drive in the commercial vehicle sector for the foreseeable future.
In addition to the automotive industry, Albonair products are also used in stationary systems such as combined heat and power plants and power generators as well as in ships.
Urea dosing systems
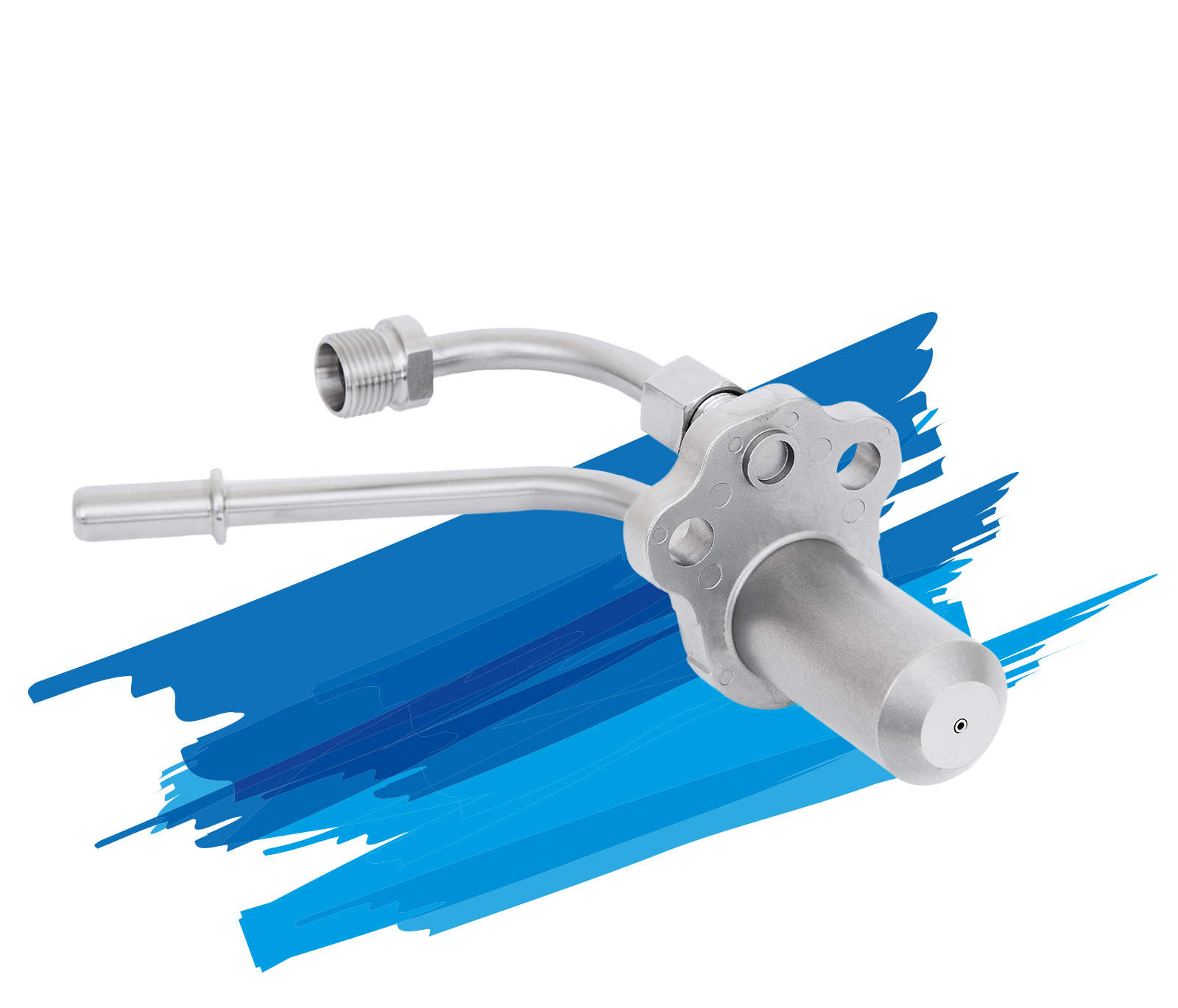
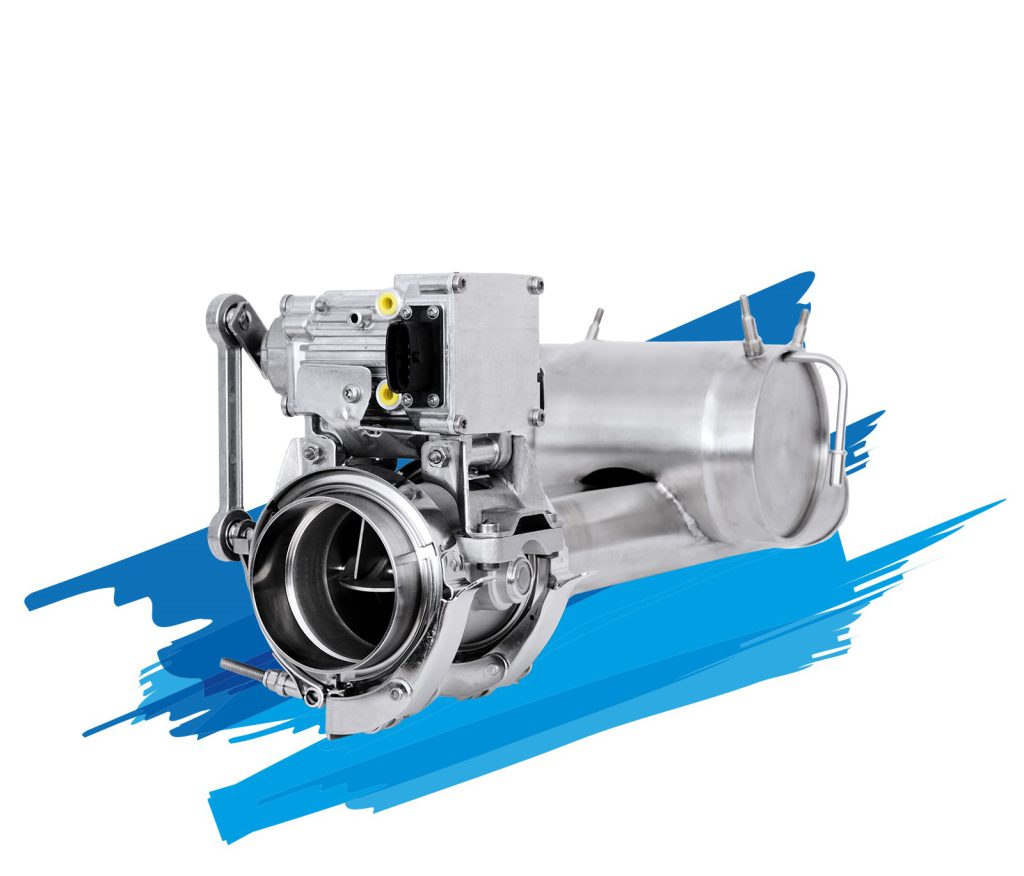
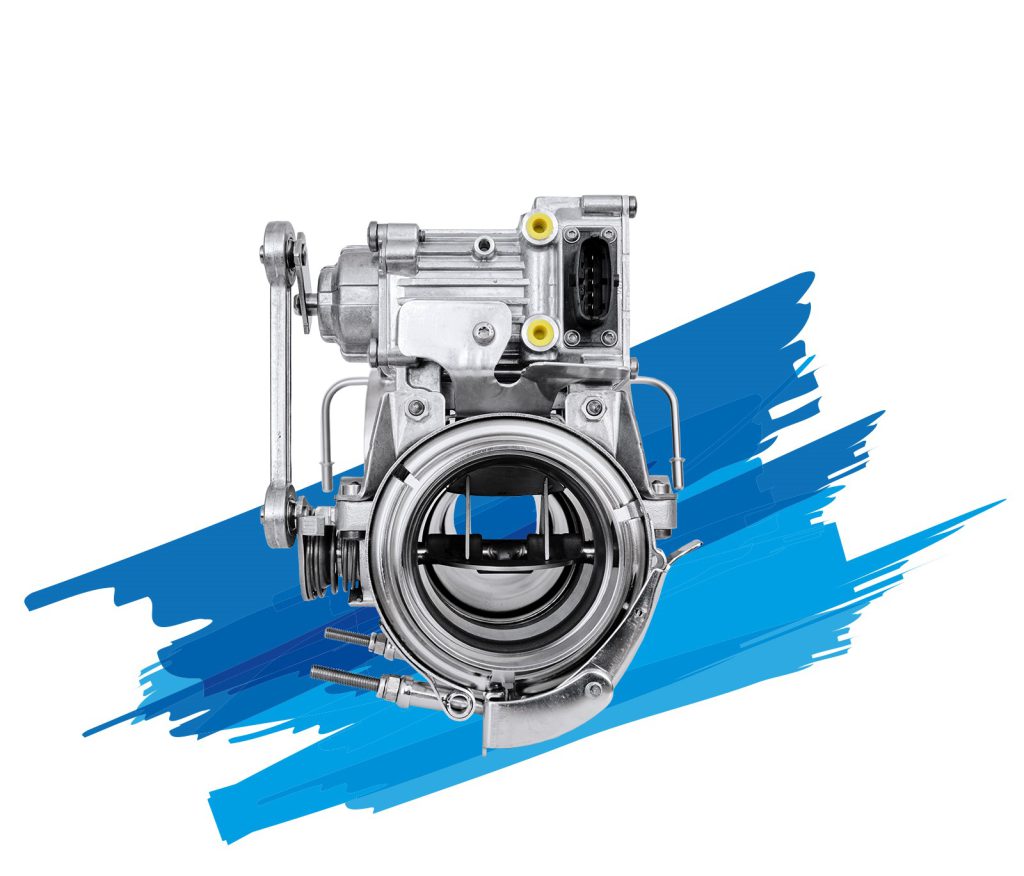
Albonair’s urea dosing systems consist primarily of two elements: the dosing unit and the injection nozzle. As a central element of SCR systems, they ensure the optimal and needs-based dosing of the AdBlue®/DEF reducing agent, an aqueous urea solution.
Albonair technology convinces with highly efficient urea processing using an ultra-fine spray and a very robust and maintenance-free design. This enables high SCR efficiencies even in the low temperature range and a significant reduction in total cost of ownership (TCO).
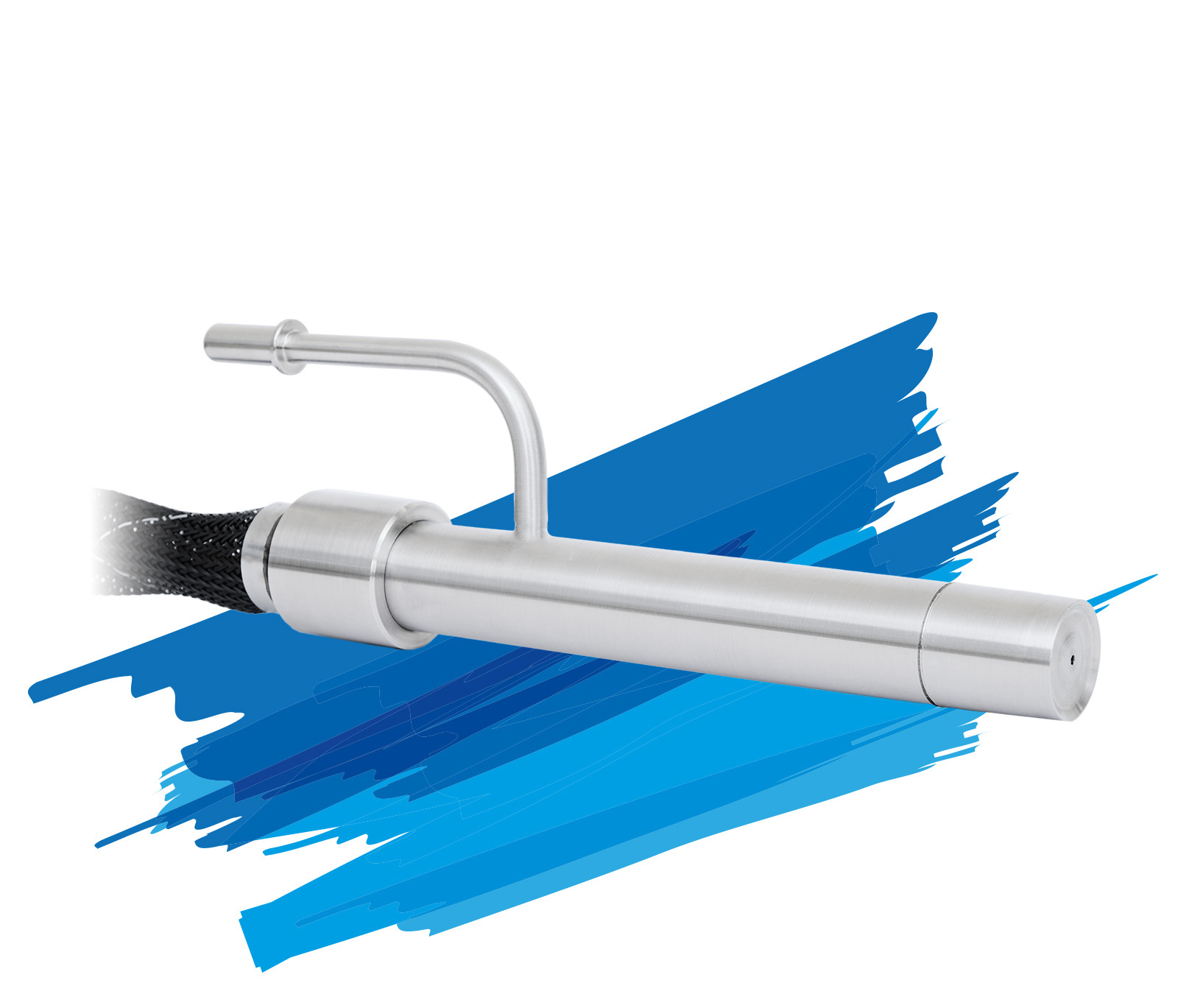
Dosing units
Our product portfolio includes various dosing units. All model variants work according to the principle of atomizing the AdBlue®/DEF with the help of compressed air.
Our dosing units feature a robust, maintenance-free design and precise dosing technology. Depending on the model, they can dose up to 7.2 kg/h or up to 10.8 kg/h with a dosing accuracy of ±5 percent. In the event of frost, the dosing units are heated via the engine cooling water.
Thanks to the different dosing and suction line lengths and the possibility of installing the dosing unit at different heights to the nozzle and the urea tank, the Albonair systems offer great flexibility with regard to the installation variants in the vehicle.
Our dosing units can be controlled either via an Albonair control unit or the customer’s own control unit.
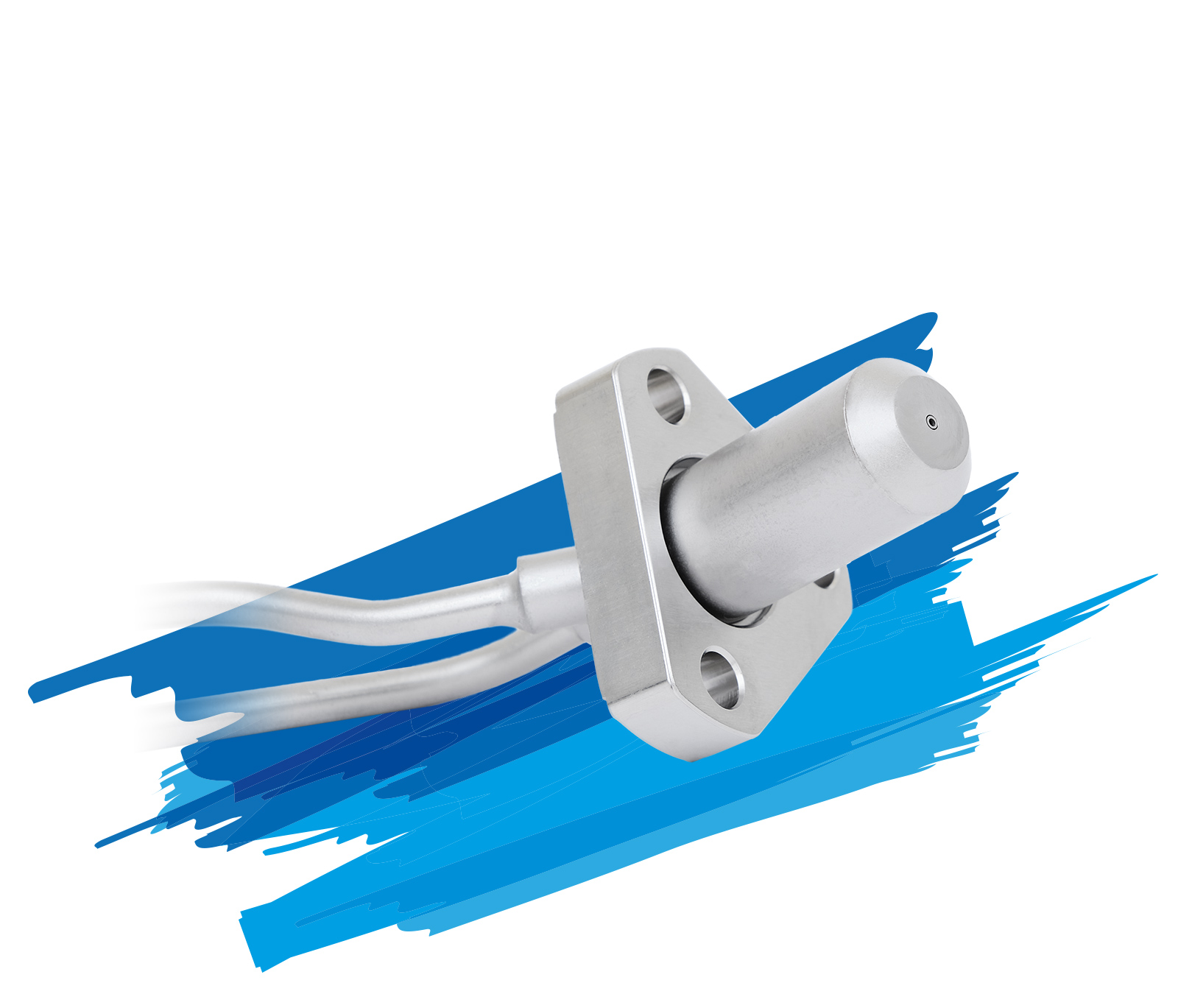
Albonair offers customers a wide variety of nozzle types depending on the application. Our portfolio includes two-substance nozzles with separated channels for media, air and AdBlue®/DEF as well as an electrically heated nozzle.
Two-substance nozzles
Albonair relies on air-assisted, external mixing systems in which the AdBlue®/DEF is atomized in the exhaust system with the help of compressed air. The two-substance nozzle technology means that the media air and AdBlue®/DEF are not mixed until they reach the nozzle outlet. This principle minimizes the risk of line blockages and ensures a particularly fine spray pattern with a Sauter diameter (SMD) of less than 15 µm. The reducing agent evaporates directly in the exhaust pipe.
Heated nozzle
Albonair’s electrically heated nozzle ensures that the AdBlue®/DEF reducing agent is already heated and vaporized in the injection nozzle. Even at low exhaust gas temperatures, the processing of the reducing agent, its distribution and chemical pre-reactions are promoted and comparatively high SCR catalytst efficiencies are achieved with minimal energy consumption for heating. That way, the nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas can be effectively reduced even at low exhaust gas temperatures, for example when driving in the city. Lowering the minimum operating temperature of the catalyst leads to lower CO2 emissions, especially for operation in urban areas.
All Albonair nozzles feature a robust and compact design, which does not require any moving components or sensors. As a result, they can be positioned in thermally hot zones of the exhaust system without any problems. The nozzles do not overheat and do not require active cooling. This is particularly beneficial for systems with active regeneration. In addition, Albonair nozzles are maintenance-free.
Since there is no risk of the nozzle overheating, our urea dosing systems can deliver at a constant dosing frequency without interruption. As a result, AdBlue®/DEF is continuously metered into the exhaust system at all operating points of the engine, so that a high level of nitrogen oxide conversion is achieved.
Thermal management systems
Together with a development consortium*, Albonair has developed an exhaust gas temperature management system called CatVap®. This is intended to counteract the problematic emission behavior at low exhaust gas temperatures caused by low driving speeds, which occurs primarily in inner-city areas.
The aim of the new system is to heat the exhaust gas cleaning system to operating temperature within 20 seconds after a cold start and to keep the working temperature of the exhaust gas cleaning system at a level above approx. 220° C, regardless of the engine’s operating status. This enables pollutant conversion with an efficiency of almost 100 percent.
For this purpose, fuel is fed into the CatVap® system, which is catalytically cracked and oxidized. On the one hand, the reaction enthalpy released in the process is used directly to heat the exhaust gas system. On the other hand, with an increased fuel supply to the CatVap®, synthesis gas is generated, which is further oxidized in the oxidation catalyst (DOC) of the exhaust aftertreatment system. In addition to the thermal advantage of the exhaust aftertreatment, the chemical activity of the DOC is also significantly increased.
The system is operated in close interaction with the combustion engine in such a way that the pollutant emissions of the drive are minimized and the fuel consumption for the heating measure is optimised.
* Development consortium: Albonair GmbH, Vitesco Technologies, Thomas Magnete, Frauenhofer ISE
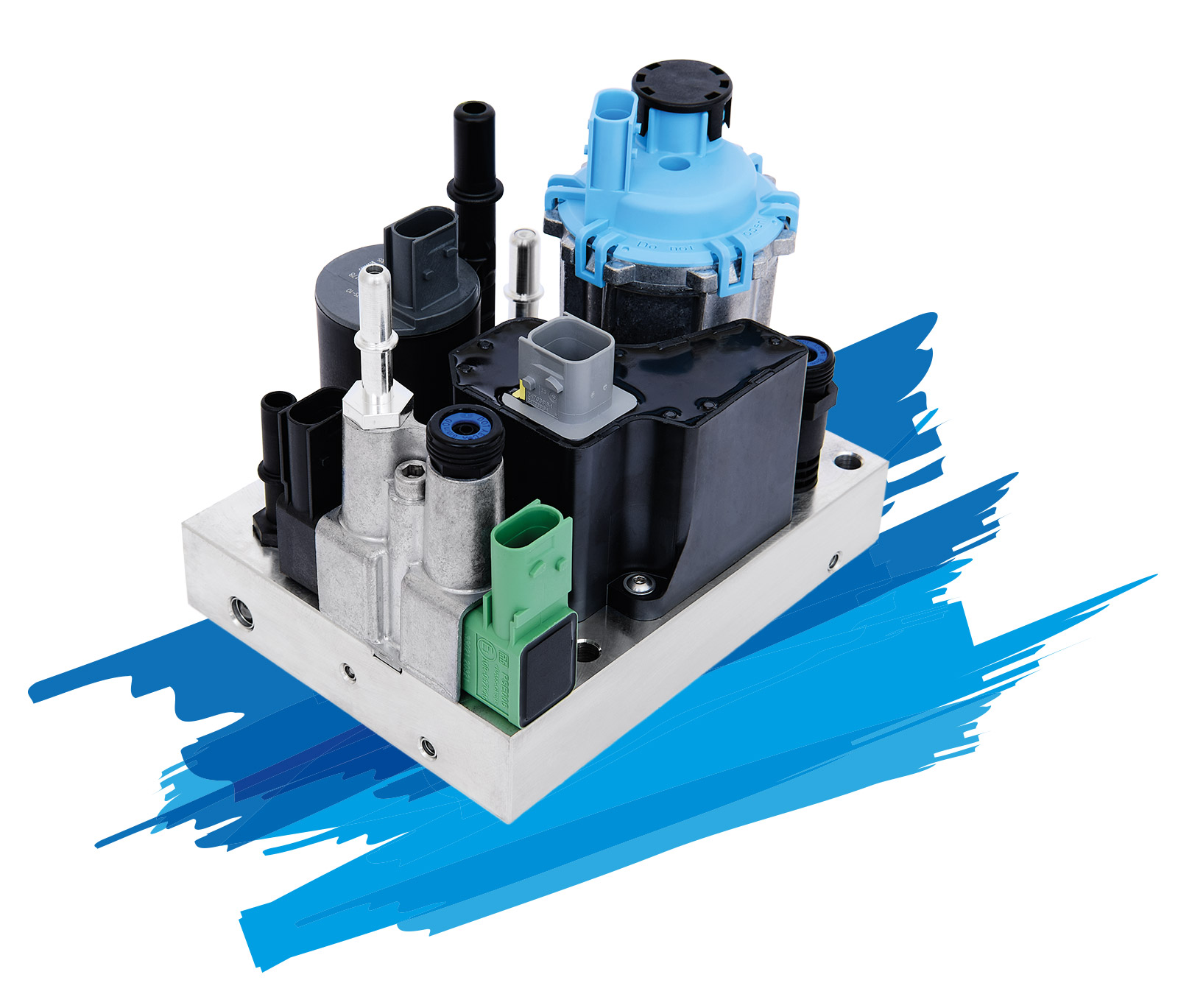
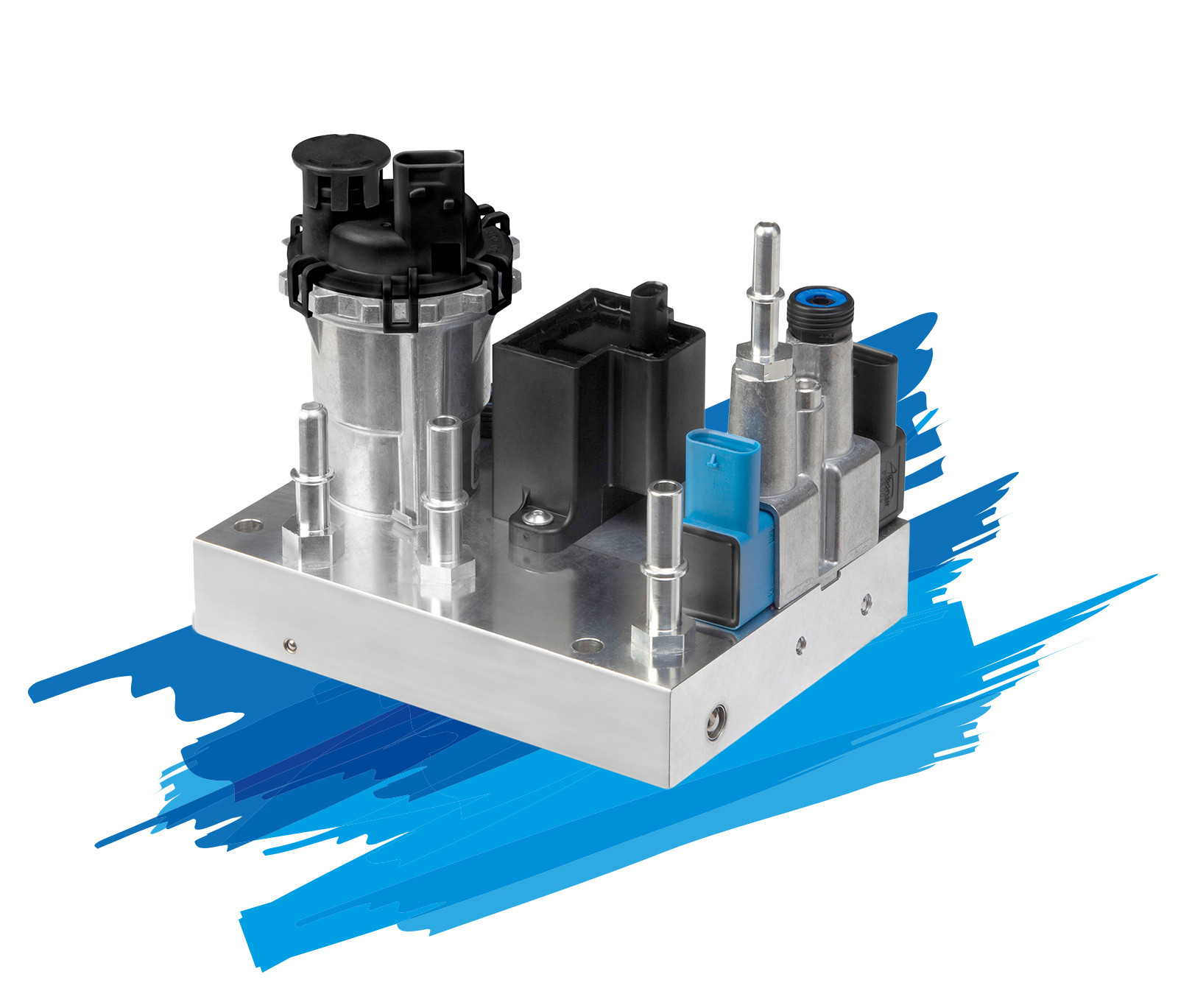
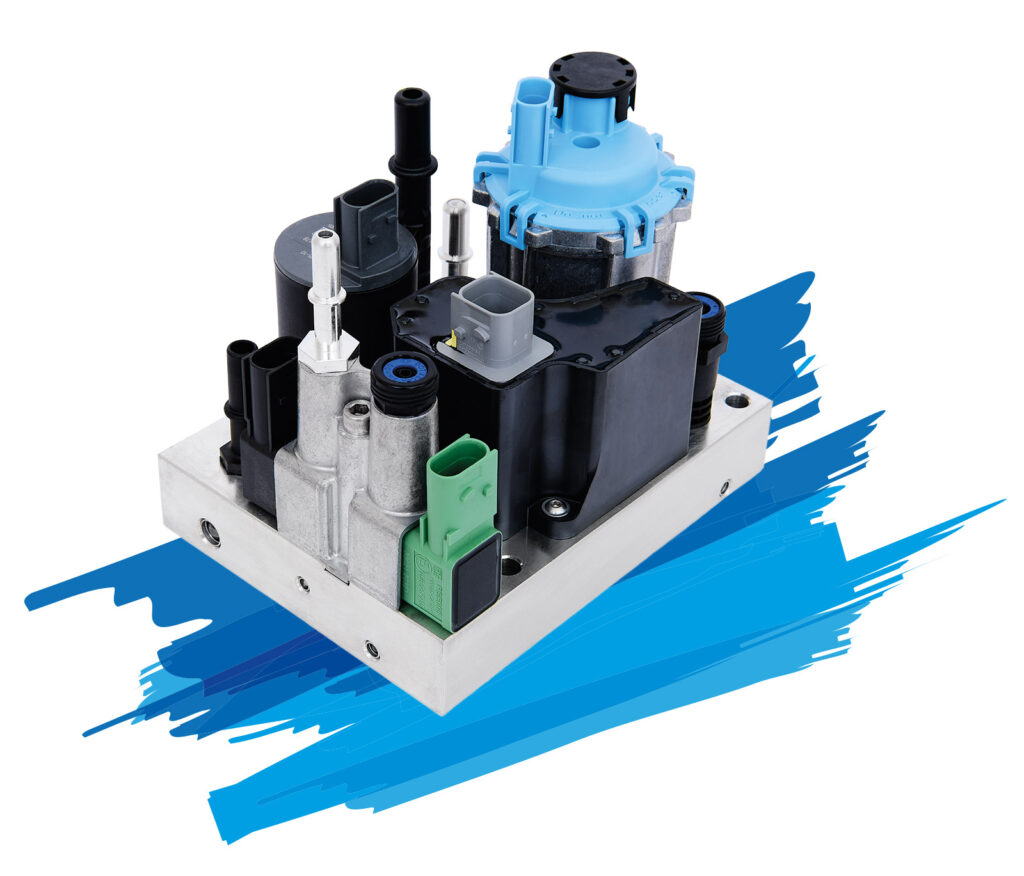
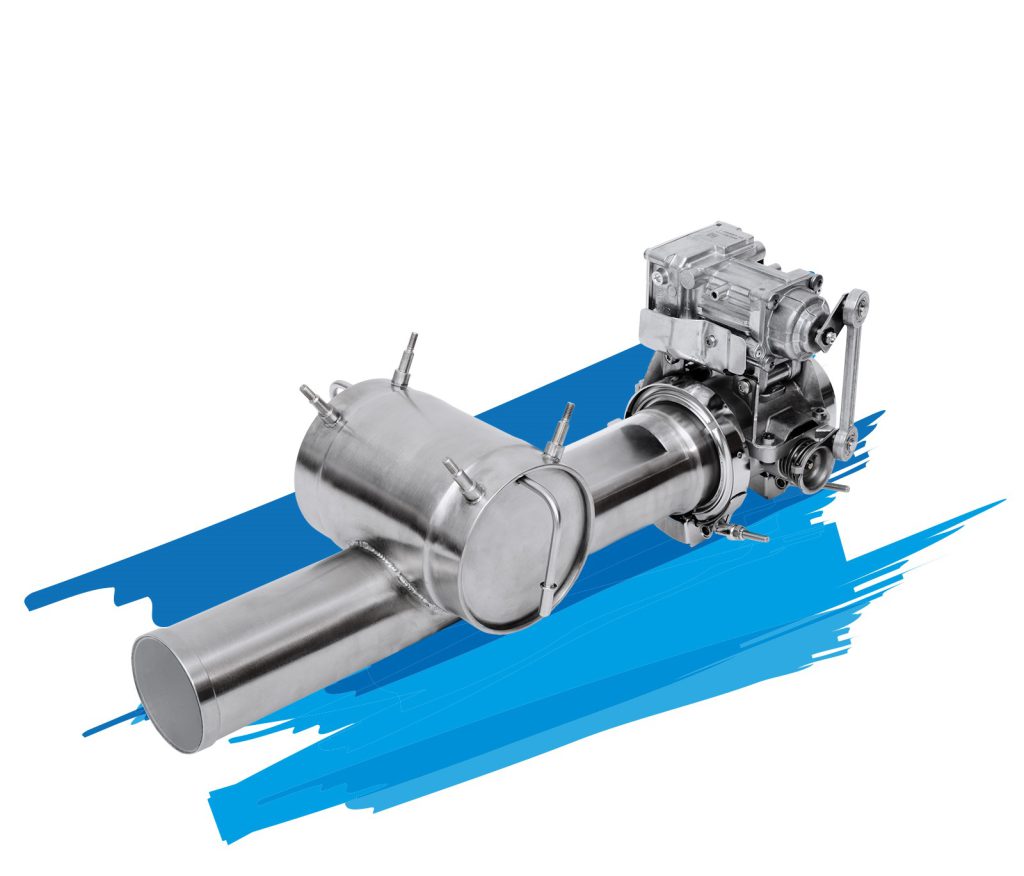
Systems for stationary Systems
Under the generic term StationAir, Albonair has an exhaust aftertreatment system in its product portfolio that was specially developed for off-road applications. Typical areas of application are mobile work machines, power generators, CHPs and marine applications.
The components for this completely modular system are the proven Albonair products from the automotive sector with dosing unit, nozzle and tank system. Due to the modular design, the system can be precisely adapted to the requirements of the application. In addition, there is the option of using only individual components of the system and combining them with your own components.
Central control is via a display (HMI) that can be used as a human-machine interface. It is used to call up the system status and to calibrate a large number of parameters in order to optimally adapt the system to the respective application.
With the controller, it is possible to control up to eight dosing units connected in parallel, so that a total dosing quantity of up to 80kg/h can be achieved and even large exhaust pipe diameters can be evenly supplied with urea.
Memberships
Albonair is a member of a variety of research associations. Our aim is to make the internal combustion engine more environmentally friendly and thus make a contribution to sustainable mobility.
Our managing director Dr. Georg Hüthwohl is a member of the Board of FAD e.V. (Förderkreis Abgasnachbehandlungstechnologien für Verbrennungskraftmaschinen).